Improving donor trust through impact stories on Shortage
Role
Product Designer (pro bono)
Timeline
Fall 2022
Industry
Nonprofit tech
Platform
Web
TL;DR
Testing whether story-driven content could improve donor trust and increase conversions
ShortageUA wanted to understand whether adding impact stories to donation flows could improve trust, strengthen transparency, and ultimately increase successful donations. Tanya and I led user research, journey mapping, and concept validation to evaluate this opportunity. Two rounds of comparative testing showed that while stories improved emotional engagement, they did not meaningfully increase perceived trust or usefulness. The findings revealed that donors rely more on operational transparency and credibility signals than on narrative content alone — shaping clear recommendations for where the platform should invest next.
Note: This case study is based on a pair-design exercise recorded with my partner Tanya Zavialova as part of the first edition of the Product Design Fundamentals course. The complete walkthrough and research discussions are available on YouTube (in Ukrainian).
Context & Business need
ShortageUA connects donors with urgent needs for medical and humanitarian goods across Ukraine. The platform’s ability to operate sustainably depends on donor trust — without clear legitimacy signals, many first-time visitors hesitate or fail to complete a donation. Although the team believed that inspiring stories might increase trust and strengthen donor engagement, it was unclear whether narrative content would meaningfully influence donor decision-making.
To make an informed investment decision, ShortageUA needed evidence: Would adding impact stories increase donor trust, clarify operations, and lift donations enough to justify the effort of producing and maintaining richer narrative content?
Tanya and I led a rapid research-and-validation track to answer this question. Through qualitative interviews, journey mapping, and two rounds of structured comparative testing, we evaluated whether stories improved trust, usefulness, and ease of use — and whether they addressed the core trust barrier in the donation flow.
Research approach
To understand what shapes donor trust in volunteer platforms, we conducted:
A survey of 27 members of the Ukrainian diaspora and foreign supporters.
Interviews with active donors.
Interviews with volunteers who receive and distribute goods.
Our research revealed several consistent patterns:
What donors value
Operational legitimacy and clear financial transparency
Verified partners and recognizable institutions
Evidence that logistics are reliable
Clear breakdown of how donations are used
Where uncertainty appears
Unclear sourcing and delivery routes
Lack of visible operational partners
Hesitation around whether the funds reach the intended recipients
What stories influence
Emotional connection
Empathy and motivation
Perception of impact
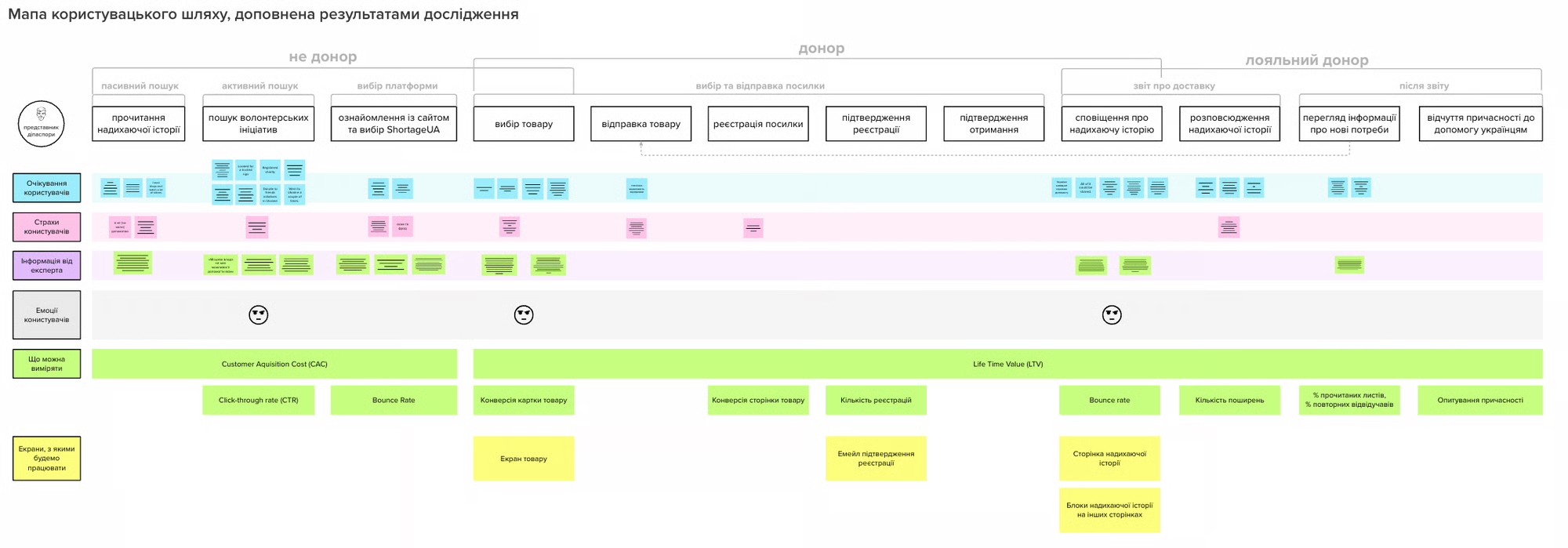
Across interviews, donors expressed that stories were inspiring — but not a substitute for institutional trust signals such as verified deliveries, audit logs, or financial reporting. To identify where storytelling could strengthen trust, we recreated the end-to-end user journey and facilitated a workshop with the client to align expectations and uncover opportunities. This insight shaped the direction of our design exploration.
Design concept
To test whether stories could meaningfully shape trust, we developed two concepts:
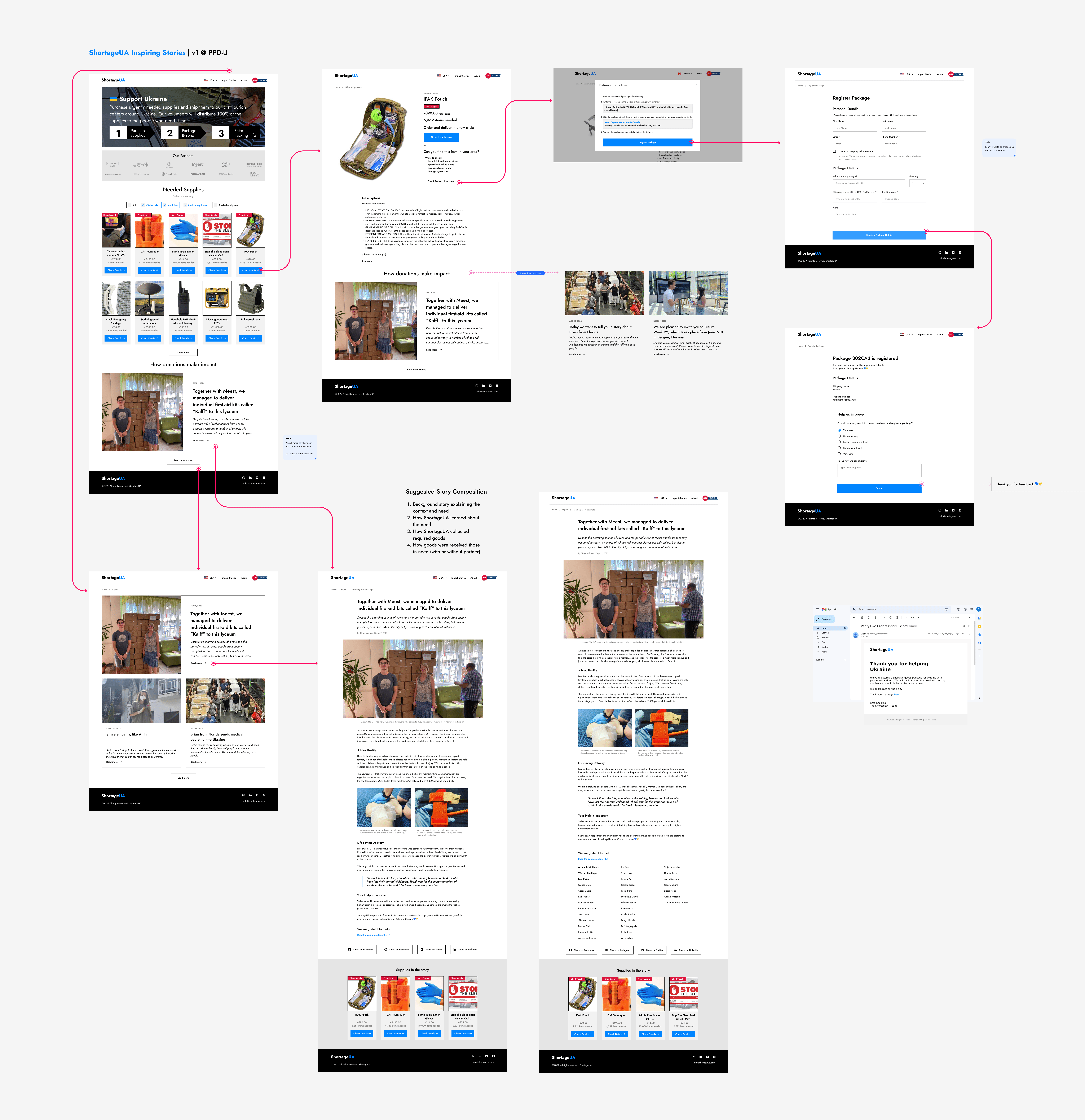
Control flow: A simplified donation journey focusing on operational clarity.
Story-augmented flow: A version that introduced inspiring user stories early in the journey and reinforced them before the donation step.
The redesigned flow aimed to:
Increase emotional engagement.
Make the value of donations more tangible.
Surface calls to action in meaningful context.
Maintain anonymity options for donors who preferred privacy.
The flow diagrams below illustrate where storytelling elements were introduced and where trust validation happened.
Key interaction moments
To identify trust-trigger points, we mapped the donor journey end-to-end:
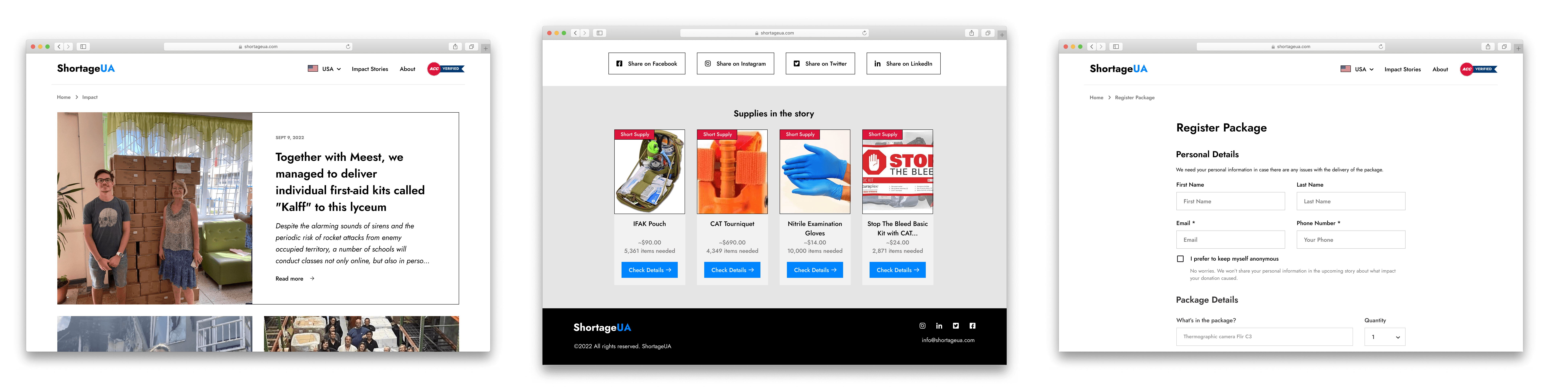
Users begin by reading authentic stories from volunteers and recipients.
Calls to action are positioned after emotional engagement.
The donation flow keeps anonymity as an explicit, reassuring option.
Operational details reinforce legitimacy before the final donation step.
Emotional resonance occurs at the beginning of the journey, while credibility and transparency must anchor the decision near the end. This mapping helped identify where narratively rich content could be effective — and where its impact would likely diminish.
Concept validation
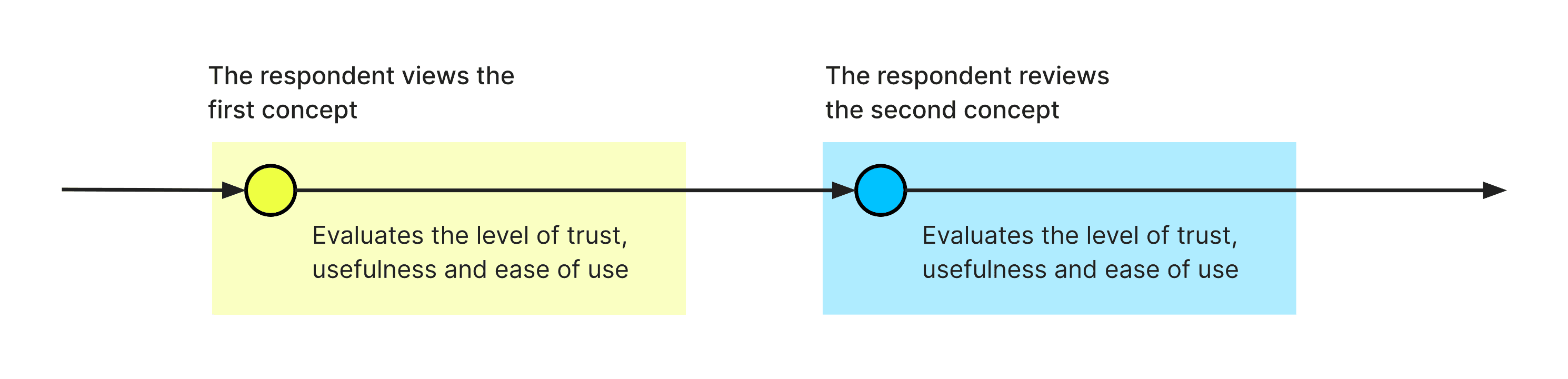
We ran two rounds of comparative testing, measuring three critical attributes:
Perceived trust
Usefulness
Ease of use
Each metric was scored on a 1–5 scale.
Round 1: Moderated testing (2 participants).
Round 2: Unmoderated testing (11 participants).
Participants evaluated both flows (with and without inspiring stories).
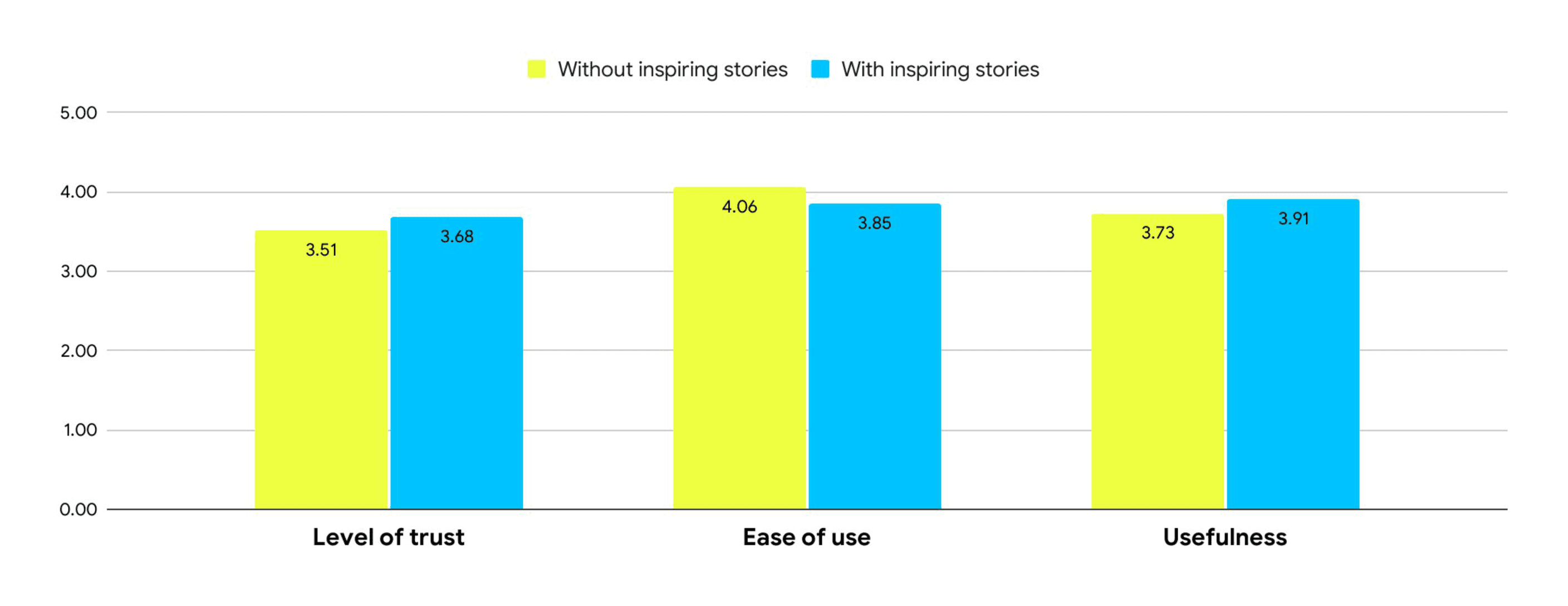
Results
Stories did not significantly increase perceived trust.
Stories did not improve perceived usefulness.
Stories did not improve ease of use.
Donors continued to rely on operational transparency over narrative content.
In both rounds, participants said they appreciated the stories but still needed more concrete, verifiable information before donating.
Conclusions
Our research showed that while impact stories made the experience more engaging, they did not significantly increase donors’ perceived trust, usefulness, or confidence in the platform. Donors consistently valued transparency — verified operations, clarity of logistics, and institutional credibility — more than emotional storytelling. Stories enriched the experience, but they did not address the primary barrier preventing donations.